Bitcoin Breaches Psychological Level of $30K amid Dollar Index Slipping
After printing nine consecutive weekly red candles, a scenario not seen in its 13-year journey, Bitcoin (BTC) is back to winning ways after topping the psychological price of $30,000.

After printing nine consecutive weekly red candles, a scenario not seen in its 13-year journey, Bitcoin (BTC) is back to winning ways after topping the psychological price of $30,000.

The leading cryptocurrency was up by 5.42% in the last 24 hours to hit $30,648 during intraday trading, according to CoinMarketCap.
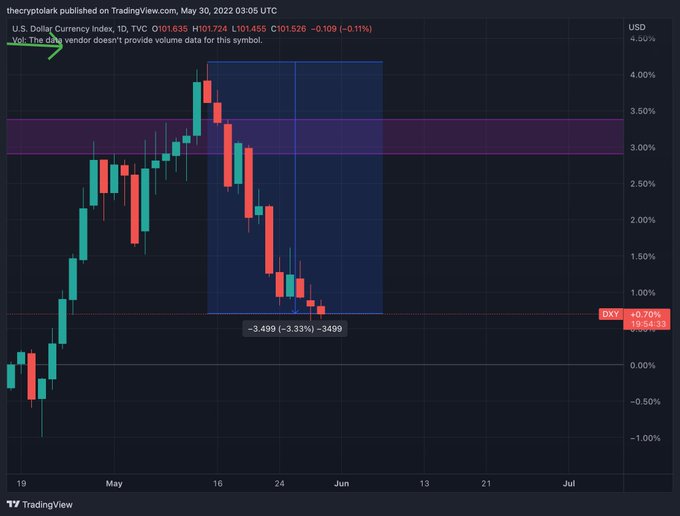
This price increase is experienced amid the falling US Dollar Index (DXY). Market analyst Lark Davis pointed out:
“The Dollar Index DXY is falling. Historically this is good for Bitcoin in the opposite way that Dollar rallies are bad for BTC price.”
Source:TradingView
With market analysis showing an inverse relationship between the DXY and Bitcoin, it remains to be seen whether this will trigger the much-needed momentum in the BTC market for a further price surge.
For instance, as Bitcoin soared by more than 295% in 2020, the DXY hit a 32-month low.
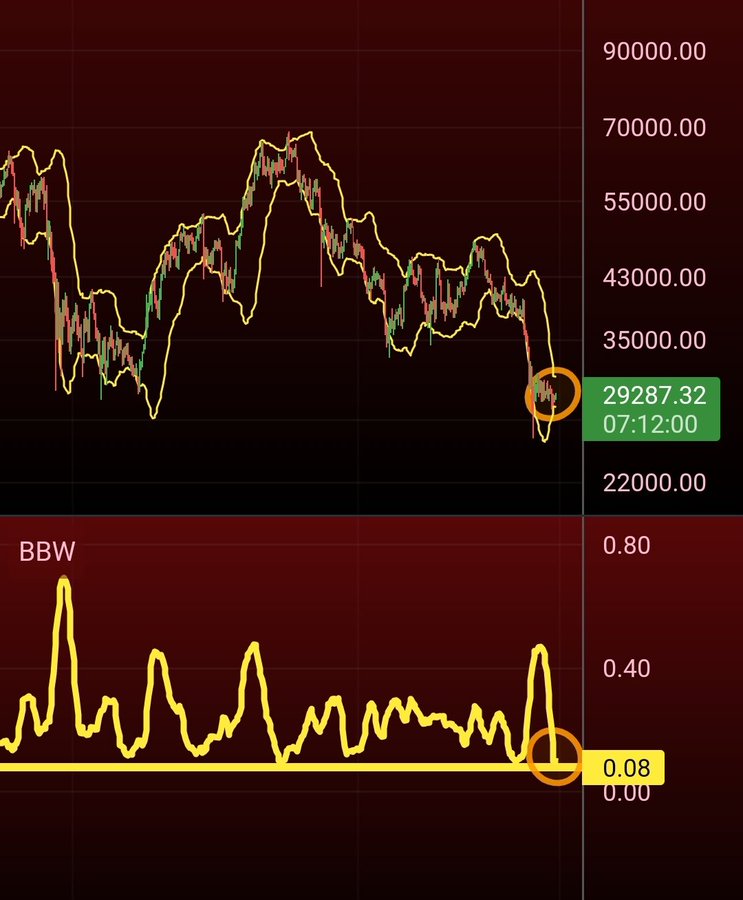
Bitcoin’s daily Bollinger Bands tighten
On-chain analyst Matthew Hyland believes the Bitcoin market might be experiencing the calm before the storm because the daily Bollinger Bands (BB) have squeezed to levels not seen in a year. He explained:
“Bitcoin daily Bollinger Bands are the tightest they have been in the past year. The Bollinger Bands Width (BBW) displays this. Buckle up, everyone.”
Source:Matthew Hyland
Bollinger Bands are a popular technical indicator developed by John Bollinger, which shows a market’s volatility. They are also used to indicate overbought and oversold conditions in the market.
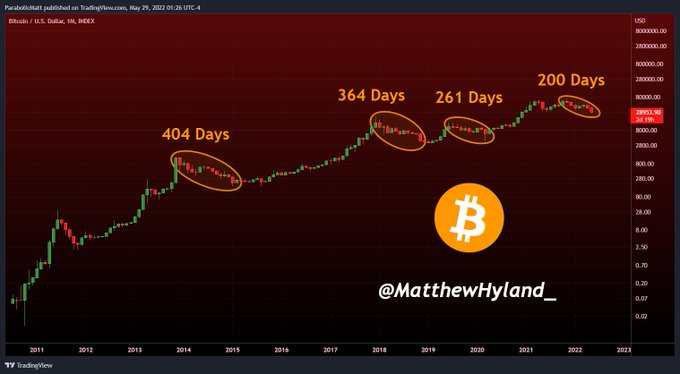
With Bitcoin currently experiencing its 4th longest downtrend in its entire history, Hyland believes a reversal is imminent.
Source:TradingView
A crypto analyst under the pseudonym PlanB recently echoed similar sentiments, given that the moving average (RPMA) and relative strength index (RSI) indicators were at extremely low levels.
Image source: Shutterstock


.jpg)